In June of this year, Google began implementing their new update of how they rank pages. This update, known as Core Web Vitals, uses a set of specified factors that Google deems important to a webpage’s user experience. These factors measure loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
As marketers, these changes are important because they affect a webpage’s Google search engine ranking. This makes it necessary to ensure that your website is performing well when it comes to these Core Web Vitals. Otherwise, you risk losing out to your competition due to a poor search engine ranking and a below par user experience.
In this post, we take a deeper look at the factors that make up Core Web Vitals and how they affect your company’s website.
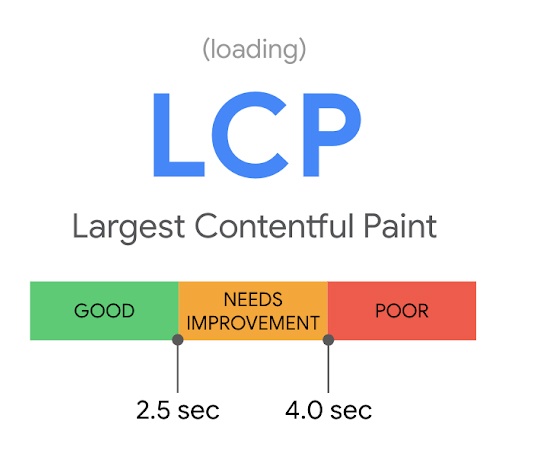
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
What Is It?
The first Core Web Vital is Largest Contentful Paint. LCP refers to the speed at which the main content of a webpage loads. When a user clicks on a link to your webpage, LCP is the time it takes for the content on that page to show to the user. A good LCP score means that your webpage loads in 2.5 seconds or less.
How It Affects Your Site
Largest Contentful Paint plays an impactful role when it comes to large webpages or webpages that have lots of high quality images or features, since they usually take longer to load.
Besides simply removing the larger files from your site, there are other ways to improve your LCP score. One way is to implement lazy loading. Lazy loading means that images will load only when a user scrolls down to it, rather than at the time that user clicks the link to your page.
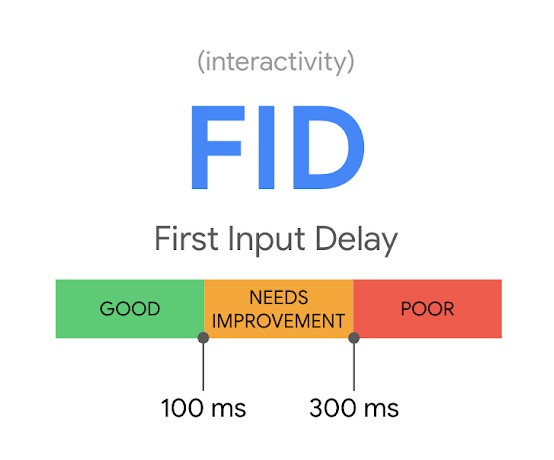
First Input Delay (FID)
What Is It?
First Input Delay, or FID, measures interactivity. Specifically, it measures how long it takes for your webpage to respond when a user interacts with it. Examples of interactions include things like clicking a button or zooming in on an image. To have a good FID score, Google requires that your site reacts to user activity in less than 100 milliseconds.
How It Affects Your Site
FID plays a large role in webpages where users need to click on something or perform an action as soon as the webpage loads. A typical example would be a log in page or a sign up page. For those types of webpages, it is better if users can start typing their information quickly without having to wait for your webpage to process their actions.
Ways to improve your FID score include minimizing your webpage’s JavaScript and/or using a browser cache.
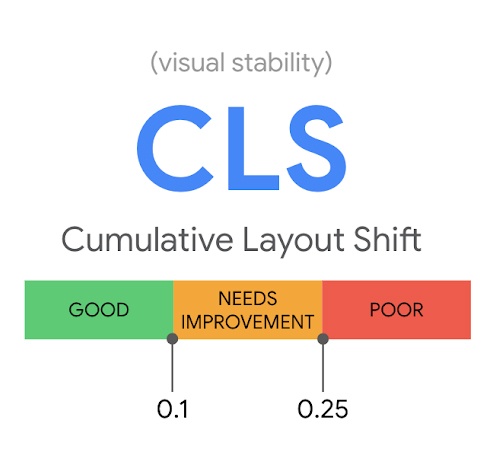
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
What Is It?
Cumulative Layout Shift measures how stable the elements on a page are while the page is loading. Another way to think of it is that as a webpage loads, CLS measures how much images and links on that page shift. CLS score is affected by two metrics, the impact fraction and the distance fraction. Your webpage’s CLS is the product of multiplying the two fractions. Without getting too technical, the impact fraction measures the total visible area of an element if it shifts, while the distance fraction measure the greatest distance that an unstable element has shifted. Overall, a good CLS score is 0.1 or less.
This article gives a good explanation of how Cumulative Layout Shift is calculated if you are interested in learning more.
How It Affects Your Site
If the elements on your webpage are shifting, it interrupts the user experience because users may end up clicking on an unintended link, image, or button that shifted as the webpage was loading. This can be frustrating for users since these accidental clicks are taking them to pages they had no intention of ever viewing.
To improve your CLS score, it is important to use set attribute dimensions for videos, images, infographics, and any other type of media on a webpage. This will make it so that the media will not shift or change in size as the page fully loads. Another tactic would be to make sure ad elements have a designated space on the webpage. This will prevent ads from causing elements to shift after the webpage finishes loading.
Conclusion
With Core Web Vitals, Google has made it clear that they are prioritizing user experience when it comes to their search engine rankings. The best place to start improving on these factors is to test your website using the Core Web Vitals report available through Google Search Console. Once you know how your website scores in each factor, you can begin to take actions to improve them. The improvement process may take a lot of time and resources, but it will be worth it in the long run.
If you have concerns or need help improving your website’s Core Web Vitals, contact us to schedule a consultation.
The post Google Core Web Vitals: How It Affects Your Website appeared first on Durham Digital Marketing Agency.